- Essay One: How can metaphors be used as a research tool? What are the advantages and disadvantages of using metaphors for research? Elaborate and justify a metaphor for the use of social media such as Facebook.
- Essay Two: How do you define IS adoption/implementation success? How do you measure this success? List and discuss three of each advantages and disadvantages of these measurement approaches? Are these measures influenced by the mobility of the system? Provide examples to justify your answers.
Essay One
Topic: How can metaphors be used as a research tool? What are the advantages and disadvantages of using metaphors for research? Elaborate and justify a metaphor for the use of social media such as Facebook.
Lecturer’s Name: Tiong Goh & Kristijan Mirkovski
Date: 21st June, 2017
Word Count: 1532
Introduction
Metaphor as a cognitive phenomenon, and it has extremely extensive impact on human thinking, artistic creation, and language use. Metaphor based on another experience to understand and experience a thing. Specifically, through the comparison of similar attributes, metaphor often uses familiar, simple, concrete, intuitive, well-known concept or thing to explain and describe another new, complex, abstract, unknown concept or thing. The purpose of using metaphor is making the concept or thing easier be identified, communicated, understand and remember. It probably says metaphor is the mapping between the real world and the abstract world. Using metaphors in research could provide a unique opportunity to understand the actual phenomenon within research experiments. The use of metaphors as a research tool could help researchers reduce a huge amount of resources to easily clarify their ideas in context.
Neergaard & Ulhøi (2006) introduced that there have four advantages and four disadvantages if using metaphors in a research. The advantages of using metaphors including: firstly, using metaphors could inspire people think different ways, for example, the function of metaphor is make complex thing simple, which it can help people think more creativity. Secondly, using metaphors could help readers easily to understand the research, because metaphor is usually a phase that everyone could understand. Thirdly, using metaphor could attract people to read, for example, the first sentence in an introduction should capture readers attention, and attract readers want to read more about this topic. Finally, using metaphor could help the article influence the people’s emotion, because metaphor could have multi-layer meanings. The result is using metaphor not only to help researchers better express what they want to present, but also can help readers to gain a better understanding of the article. On the other hand, the disadvantages of using metaphors including: firstly, using metaphors could make researcher confused about the topic, because if researcher misuse the metaphors, it will cause misleading people’s point of view. Secondly, using metaphors may make the topic difficult to understand, because use metaphor in research is not focus on the topic, and it normally used to help reader to understand. Thirdly, using metaphors might attractive enough to let readers want to read, but it might let readers feel that this article is not the article they want, because it did not show the subject of the study at the beginning. Finally, using metaphors might lead to less focus on the topic, and probably have poor logic in the article.
Discussion
In my opinion, we could use metaphors as an artefact in research, or we could use it as an inspiration tool to inspire researcher creative thinking of the topic. In addition, we could use metaphors as a presentation tool to quickly express the ideas. However, how about using metaphor in social media, what is social media like, and how we could feel to be part of it. Social media, or social network, which stands for a group of people with the same interests and activities to create an online community. Such network often based on the Internet to provide users with a variety of contacts and exchanges with other users, such as e-mail, instant messaging services, and sharing information. As a result, the metaphor for social media (like Facebook) is like a Christmas party, where everyone invited to the party, in other words, friend’s friends are friends. People can relax their bodies and minds though parties, and play with their friends. Meanwhile, the parties provides many opportunities for various people in the social life. People can make different friends on the party, usually these friends have different culture, in the way people can learn more from different regions of the people’s culture and living customs.
In the research study, Gorry & Scott-Morton (1989) indicated that an effective framework could improve information systems efforts, in other words, use a proper framework for management information system (MIS) is the main challenge for the organization. They also shows that strategic planning, management control, and operational control are the main framework for analysis process in order to develop an effective information system within the organization. For social media study, a proper framework to study such object is necessary, and it is more like a guide to teach people how to get into the party. The function of party is to create a public environment to let people know each other’s and become a friend. Firstly, people get together to know each other’s, and then they normally will form a group of people, most of the people in this group are friends who know each other. Alternatively, they do not know each other, but they have the same interests and hobbies, or they just from the same school or company. Thirdly, they gather around within the party, and they share information to others within the group. The content of information is usually include, name, birth of year, schools, company, interests, and so on.
In addition, Hirschheim & Newman (1991) indicated that using metaphor in research is to describe the relationship between technology and users, and metaphor as a way to understand a thing in different way (or easier way). For example, they take information as a structured data, and take organization as an information. They shows that two scenarios to describe the relationship between technology and users: “technology as tool and man as craftsman” is used in an optimistic scenario, and “technology as governor and man as machine” is used in an pessimistic scenario (pp. 38-39). Both of these two scenarios are present the relationship between technology and users is like master and slave, like technology is master, and users are slave. They also shows that three metaphors widely used in Information Systems Development (ISD), which includes “Information Systems Development as a battle”, “organizations as fiefdoms”, and “man as machine” (pp. 49-50). In this case, if people have a social media account, they will ask to add friend, even they do not each other. This is explain how friend’s friends are friends’ works. People use technology to strengthen the relationship between peoples, but this relationship built above on the social media, In other words, they are actually virtual friends.
On the other hand, Kendall & Kendall (1993) shows that here has nigh metaphors in information systems, such as journey, war, game, organism, society, machine, family, zoo, and jungle. They also shows that one of function using metaphors in information system research is to help researcher develop a corporate strategy link to IT development in the organization. They also points our using metaphor is to describe one object as another, which make people easily to understand an unfamiliar item. They also listed five assumption of metaphors, (1) metaphor is the foundation of the English language; (2) basic metaphor needs someone else; (3) metaphor help us conceptualize some things in certain ways; (4) metaphors are usually kept constant, and have the basic form of experience; and (5) some inconsistent metaphors could be explain with different areas of experience. For the metaphor of the social media, party is like a small society, people exchange thoughts about an interesting topic. Moreover, Walsham (1991) shows that here has eight organizational metaphors concerning information systems practice, which take the organization as “machines, organisms, brains, cultures, political systems, psychic prisons, flux and transformation, and instruments of domination” (p. 83). He also indicated that organizational metaphors also related to the study of information systems. Social media also could explained with organizational metaphors, for instance, Walsham think organization as cultures, but we could also think social media as cultures, like discussed before, people in the party usually with different culture background, they will share their personal experience to others, and this allow people to understand particular things in distinctive ways. Like when I first came to New Zealand, my lecturer encourage me to take birthday or Christmas parties to understand what Kiwi culture is, there is no doubt through parties could help me learn English to quickly get into different cultures and also get to know more friends.
Conclusions
The importance of metaphor in the research can be debated, but what is fact is that there were many benefits using metaphor in the research that help people to know the topic quickly, and to help people quickly get into the scene of experiment. The case of social media that we discussed is social media is like a Christmas party, which let people to share their thoughts or information to others, to engage with others, and to talk about topic that fit the current situation. Social media, like Facebook, people could share their information to public or just to friends, and they could re-share other’s post. This makes the dissemination of information more extensive and faster. People within social media is more like every individual node within the network, where network is the connection link to keep people together. Like a party we talked before, it used to strengthen the connection between peoples. However, using party as metaphor for social media is not a proper way to describe, because there have different kind of social media exists on the network. Researcher may use a metaphor to one specific social media, but not for entire social media system.
References
Gorry, G. A., & Scott-Morton, Michael M.S. (1989). A framework for management information systems. (SMR Classic Reprint). Sloan Management Review, 30(3), 49.
Hirschheim, R., & Newman, M. (1991). Symbolism and information systems development: Myth, metaphor and magic. Information Systems Research, 2(1), pp.29-62. doi: 10.1287/isre.2.1.29
Kendall, J. E., & Kendall, K. E. (1993). Metaphors and methodologies: Living beyond the systems machine. (Technical). MIS Quarterly, 17(2), 149.
Neergaard, H., & Ulhøi, J. (2006). Handbook of qualitative research methods in entrepreneurship. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar.
Walsham, G. (1991). Organizational metaphors and information systems research. European Journal of Information Systems, 1(2), 83-94. doi: 10.1057/ejis.1991.16
Essay One
Topic: How do you define IS adoption/implementation success? How do you measure this success? List and discuss three of each advantages and disadvantages of these measurement approaches? Are these measures influenced by the mobility of the system? Provide examples to justify your answers.
Lecturer’s Name: Tiong Goh & Kristijan Mirkovski
Date: 21st June, 2017
Word Count: 1520
Introduction
How to measure IS adoption/implementation success is become a major problem in information system field. There have two ways to measure how success of IS adoption or implementation: one is to measure the performance of IS itself, and another is to measure IS on the impact of corporate performance and evaluation of the results. In my experience, I would use IS performance to measure the success of IS adoption, because it probably the best way to test the adoption is success or not. The advantages of using IS performance to measure IS success is: (1) IS performance is based on the conversation between manager and employee, and it will help solve the issue very quickly, because manager could directly know where the problem is. (2) Encourage employee to work harder, because celebration of IS success could encourage employee to make the best effort at workplace. (3) Provide a structured process to both manager and employee to discuss any issues within the organization. However, thing always have double sides, the disadvantages of using IS performance to measure IS success is include: (1) the process of performance measurement is required lots of time to implement, the organization or manager should well managed the time to evaluate the process. (2) The process may discourage employee, because if there has many issues been found during the evaluation process, it has the potential to discourage employees. (3) The process of measurement should well designed without any mistakes, because if the process did not done properly, it could create a negative experience and waste time. In this essay, we will talk about how to measure IS adoption/implementation success in the organization, and we will discuss how to implement this measurement to real business case.
Discussion
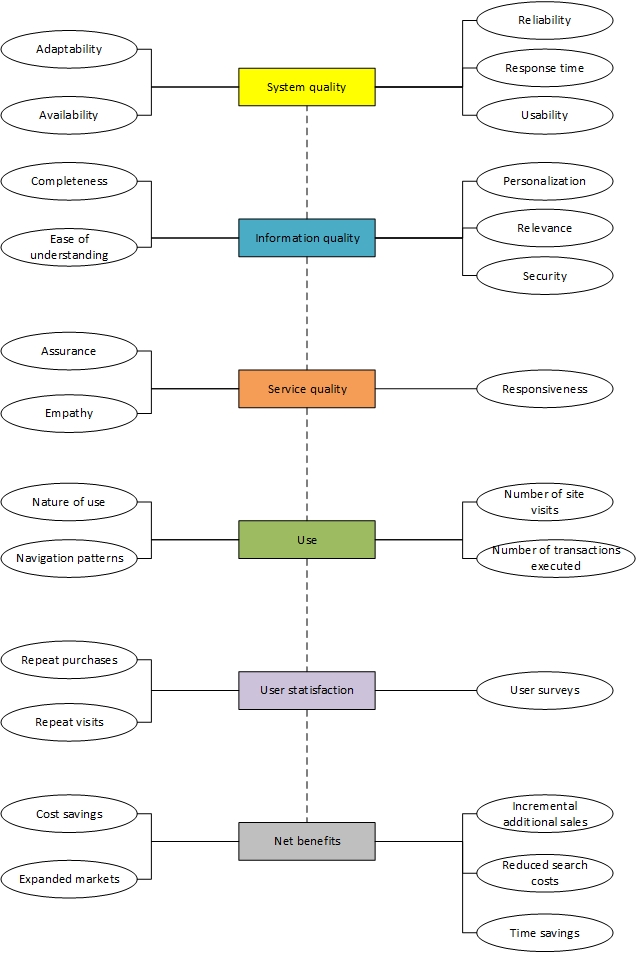
We use IS performance to measure how IS adoption/implementation is success or not, which the measurement is used at the end of IS development in the organization. Such measurement will not influenced by the mobility of system, because performance measurement is based on to measure the process and results, the process of running is to improve the organization’s goal by effectively configure the information resources, and the running results refers to the contribution of the application of information system to the realization of the organization’s goal. An example of measure Brazilian financial institution by implement the method of performance measurement, the researchers shows that the role of CIO should manage all activities that related to IT, and also they should also build a relationship between IT and organization strategy. These measurements based on survey model, the questions asked in survey is relate to relevance and success of IT results. The questions are consists four parts: cost/benefit, growth, asset and flexibility (Barbosa, Rodello & De Padua, 2014). In addition, DeLone and McLean IS Success Model was the first model to measure IS success in information system field. William & Ephraim (2003) introduced use “‘system quality’ measure technical success, ‘information quality’ measure semantic success; and ‘use, user satisfaction, individual impacts,’ and ‘organizational impacts’ measure effectiveness success” in the DeLone and McLean IS Success Model (p. 10). These six dimensions are dependent, because the level of IS success should measure by all six dimensions, each dimension is measure one aspect of IS adoption or implementation. More specifically, “frequency of use, time of use, number of accesses, usage pattern, and dependency” used to measure system use. In addition, “ease of use, functionality, reliability, flexibility, data quality, portability, integration, and importance” used to measure system quality. Furthermore, information quality measured by “accuracy, timeliness, completeness, relevance, and consistency”. Moreover, individual impact measured by “job performance, job effectiveness, decision-making performance, quality of work environment and job performance” (pp. 13-15). The model was based on D&M IS success Model to discuss how to measure IS success, there included six categories to define success of IS implementation (see Figure 1). It clearly examined how to measure IS adoption success by implement this six methods.
Figure 1: IS success metrics
Moreover, Gable, Sedera & Chan (2008) stated that system quality and information quality is used to measure the IS implementation success by using the IS-Impact Measurement Model. For system quality, it includes data accuracy, data currency, database contents, ease of use, ease of learning, access, user requirements, system features, system accuracy, flexibility, reliability, efficiency, sophistication, integration, and customisation. For information quality, it includes importance, availability, usability, understandability, relevance, format, content accuracy, conciseness, timeliness, and uniqueness.
On the other hand, Tate, Sedera, McLean & Burton-Jones (2014) indicated that type of the system and the scope of the system in IS should be considered during system evaluation, because it could affect perceptions of success. For example, people may not have such knowledge to notice the mistakes or errors in the information systems. They also shows that two popular forms of measure IS adoption success, which is self-report and user perception. They also indicated that “just ask someone” is probably a directly way to measure success of information systems (p. 5). Moreover, they also shows that service quality could also use to measure success of IS adoption, which using service to determine how IS implementation is successes within the organization. Finally, they points out measure by effective communication with stakeholders and they set a clear goal for IS project at the beginning. Moreover, Thong (1999) indicated that he use an integrated model to measure how success of information system adoption in a small business, which include four different characteristics: decision-maker, information systems, organization, and environment. Decision-maker in this case is for the role of CEO in the organization, and he shows that CEO should have ability use innovative solution to solve problems, and CEO should have basic IS knowledge to implement new technology in the organization. For information system characteristics, it should have be know better about IS attributes, because compatibility is one of major problem in the process of IS adoption. For organizational characteristics, it measured by size of business, employees’ IS knowledge, and information intensity. For environmental characteristics, competition is used to measure IS adoption, which competition is associated with adoption rates, in other words, higher adoption means it got strong competition.
From the strategic analysis of the organization, IT investment return and strategy implementation should be the most concerned about the topic. IT high risk and high failure rate requires the organization make the right decision before investment. It should conduct a fair strategic positioning, comprehensive demonstration of the advanced technology and feasibility of the project, the implementation of financial possibilities, the application of fairness and effectiveness. Compared with the traditional performance evaluation, information performance evaluation have a higher complexity. The indicators of traditional project value evaluation are more easily be quantified, the ultimate evaluation is relatively easy, its benefits are mainly reflected in the dominant income, and IT application could affect by many variables. Therefore, the performance evaluation for information system need a comprehensive measurement method. How to ensure that the effective operation of IT systems and governance is the main factor to performance measurement based on the level of information management and control. However, many organization managers think investing in information and IT constriction projects is the only way to enhance the competitiveness of the organization and the value of the organization. As a result, information based performance is not a consequence of a post eventual reflection, which is not only relevant to the realization of the functionality of the final system (the number of products and services provided) and the achievement of the results (effectively meet the expected mission objectives), but also includes information in the implementation of the strategy, management control, project management, and comprehensive capacity, which contains operational efficiency, and the ability of sustainable development.
Conclusions
In the external macro-policy guidance and the development of IT itself, driven by the survival and development of the organization for the strategic significance of the development, the value of information on the organization also placed a high position. Although all aspects of the organisation information has achieved remarkable result, but it still face many issues. The huge gap between the actual application of information and the expectations of the organization also prompted people to have to review and evaluate the information performance and value. Informational performance evaluation should be an analytical process that reflects how IT delivers business value to achieve the missions that it given to. The evaluation of information performance is concentrated in two aspects: on the one hand, process the evaluation of the information, and then provide feedback to the organization after receive the result from the evaluation; on the other hand, take a comprehensive evaluation to the effect of information systems. The only way to build a good organization performance evaluation system is to be able to clear the degree of the organization information construction, and clarify the relationship between investment and income to ensure the organization information construction can be sufficient get their own economic benefits. To sum up, the organizational knowledge management has a significant impact on the performance of the organization. Therefore, in order to improve the performance of the organization, it is necessary to build a comprehensive organizational culture and structure.
References
Barbosa, S., Rodello, I., & De Padua, S. (2014). Performance measurement of information technology governance in Brazilian financial institutions. Journal of Information Systems & Technology Management, 11(2), 397. doi: 10.4301/S1807-17752014000200010
Gable, G., Sedera, D., & Chan, T. (2008). Re-conceptualizing Information System Success: The IS-Impact Measurement Model*. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 9(7), 377-408.
Tate, M., Sedera, D., McLean, E. R., & Burton-Jones, A. (2014). Information systems success research: the” Twenty Year Update?” panel report from PACIS, 2011. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 34(64), 1235-1246.
Thong, J. Y. (1999). An integrated model of information systems adoption in small businesses. Journal of management information systems, 15(4), 187-214. doi: 10.1080/07421222.1999.11518227
William, H. D., & Ephraim, R. M. (2003). The DeLone and McLean Model of Information Systems Success: A Ten-Year Update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9-30.